ROADSIDE LITTER: What does it say about society?
Mark Heil, M.A.Sc., Geospatial Scientist and Principal of Terradynamics GIS, LLC
A total of 8 sociological variables and their relationships to roadside litter were explored. These variables include the following: commute time, median household income, the percentage of homes without kitchen facilities, the percentage of population below poverty, educational attainment, the percentage of population under the age of 18, unemployment, and the percentage of rented homes.
Three dependent variables were investigated and include the following: roadside litter quantities, roadside littered alcohol beverage container (LABC) quantities, and percentages of LABCs within roadside litter. A random stratified sampling technique generated 120 transect points along roadsides for which the dependent variables were investigated.
The relationship between the independent and dependent variables were examined using the following statistical techniques: stepwise regression analysis, hot spot analysis, ordinary least squares (OLS) regression, and geographic weighted regression (GWR).
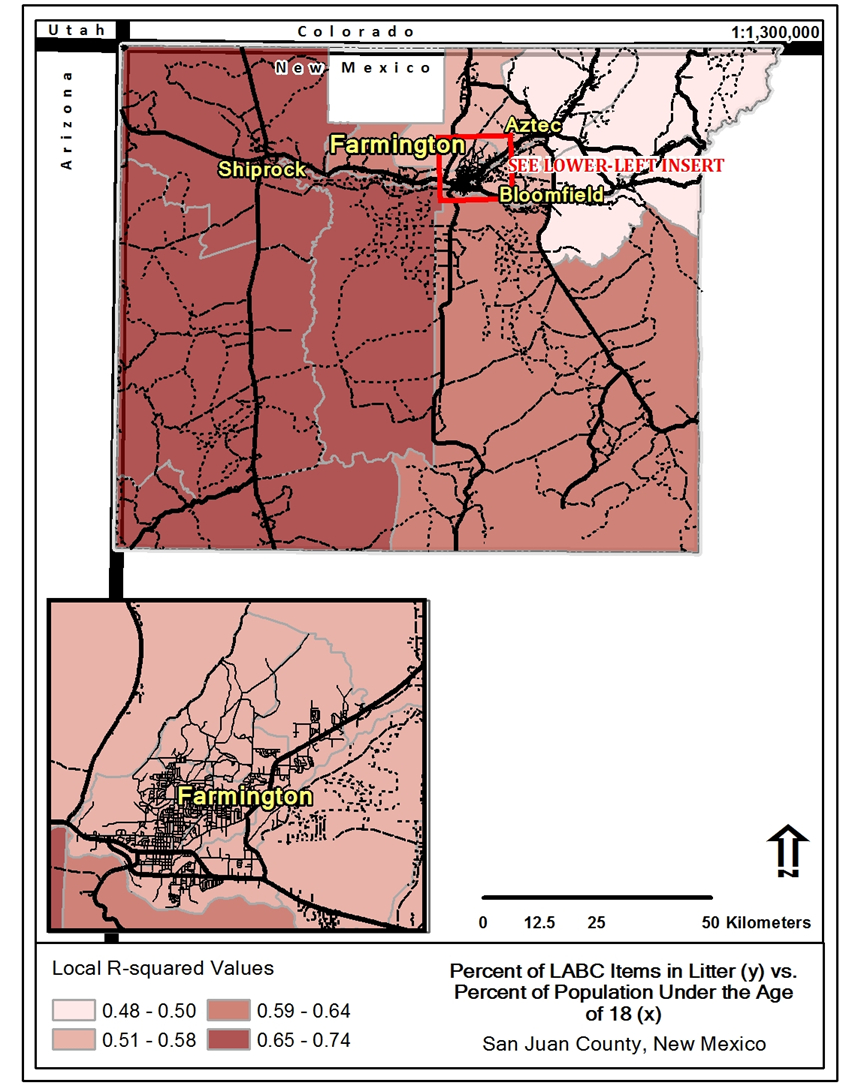
Several relationships between the variables explored were found to show significance:
1) Age, in conjunction with commute time, was shown to have a positive and stationary relationship to the percentage of LABCs occurring within roadside litter.
2) The variable of age on its own was shown to have a positive and stationary relationship to the percentage of LABCs within roadside litter.
3) Poverty was shown to have positive and stationary relationship to the percentage of LABC items within roadside litter.
This study provides general locations of high litter quantities and provides information that points to specific human behavioral spatial patterns. This information could be used to provide spatial data for law enforcement, diagnose specific social disparities, and educate specific populations about litter and the social disparities that encompass their communities.
Source:
Heil, Mark L. A Spatial Investigation of Socioeconomic Variables and Their Relationships to Roadside Litter and Littered Alcohol Beverage Containers. Thesis. New Mexico State University, 2012. N.p.: n.p., n.d. Print.